Jupyter MCP Server
by datalayer
Enables real-time interaction with Jupyter notebooks, allowing AI to edit, document, and execute code for data analysis, visualization, and multimodal output.
Jupyter MCP Server Overview
What is Jupyter MCP Server about?
Jupyter MCP Server provides a Model Context Protocol implementation that connects AI agents to live Jupyter notebooks. It streams notebook changes instantly, executes cells on demand, and returns rich outputs such as images, plots, and text.
How to use Jupyter MCP Server?
- Install dependencies
pip install jupyterlab==4.4.1 jupyter-collaboration==4.0.2 ipykernel pip uninstall -y pycrdt datalayer_pycrdt pip install datalayer_pycrdt==0.12.17 - Start JupyterLab
(When using JupyterHub, setjupyter lab --port 8888 --IdentityProvider.token MY_TOKEN --ip 0.0.0.0JUPYTERHUB_ALLOW_TOKEN_IN_URL=1and create a token withaccess:serversscope.) - Launch the MCP server – either via
uvxfor quick start or Docker for production (see configuration below). - Configure an MCP client (Claude Desktop, VS Code, Cursor, etc.) with matching
DOCUMENT_URL,RUNTIME_URL, and the notebookDOCUMENT_IDyou want to work on.
Key Features of Jupyter MCP Server
- Real‑time notebook change streaming.
- Smart cell execution that reacts to output feedback.
- Full notebook context awareness for more relevant AI interactions.
- Multimodal output support (text, images, plots).
- Multi‑notebook management – switch between notebooks within a single session.
- MCP‑compatible, works with any client that follows the protocol.
- Rich toolset (
insert_cell,execute_cell,list_files,read_cell, …) for advanced automation.
Use Cases of Jupyter MCP Server
- AI‑assisted data analysis – let a model explore, modify, and run cells to generate insights.
- Automated report generation – programmatically insert results, visualizations, and commentary.
- Interactive tutoring – AI can guide students through notebook exercises, correcting errors on the fly.
- Continuous notebook testing – run cells automatically after each edit and capture failures.
- Multi‑user collaborative AI assistants – multiple agents can operate on different notebooks concurrently.
FAQ from Jupyter MCP Server
- Do I need JupyterHub? No. The server works with any Jupyter deployment, including local JupyterLab.
- Which transport protocols are supported? Both
stdio(default) andStreamable HTTPtransports are available; see the documentation for advanced setups. - Can I run the server in Docker? Yes, Docker images are provided (
datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server:latest). The README includes platform‑specific snippets. - How does multi‑notebook support work? Set
DOCUMENT_IDto a notebook path, or omit it so the client can list and switch notebooks dynamically. - What environment variables are required? At minimum:
DOCUMENT_URL,DOCUMENT_TOKEN,RUNTIME_URL,RUNTIME_TOKEN. Optional flags likeALLOW_IMG_OUTPUTenable image handling. - Is the server open‑source? Yes, the code is hosted on GitHub under a BSD‑3‑Clause license.
Jupyter MCP Server's README
🪐✨ Jupyter MCP Server
🚨 NEW IN 0.14.0: Multi-notebook support! You can now seamlessly switch between multiple notebooks in a single session. Read more in the release notes.
Jupyter MCP Server is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server implementation that enables real-time interaction with 📓 Jupyter Notebooks, allowing AI to edit, document and execute code for data analysis, visualization etc.
Compatible with any Jupyter deployment (local, JupyterHub, ...) and with Datalayer hosted Notebooks.
🚀 Key Features
- ⚡ Real-time control: Instantly view notebook changes as they happen.
- 🔁 Smart execution: Automatically adjusts when a cell run fails thanks to cell output feedback.
- 🧠 Context-aware: Understands the entire notebook context for more relevant interactions.
- 📊 Multimodal support: Support different output types, including images, plots, and text.
- 📁 Multi-notebook support: Seamlessly switch between multiple notebooks.
- 🤝 MCP-compatible: Works with any MCP client, such as Claude Desktop, Cursor, Windsurf, and more.
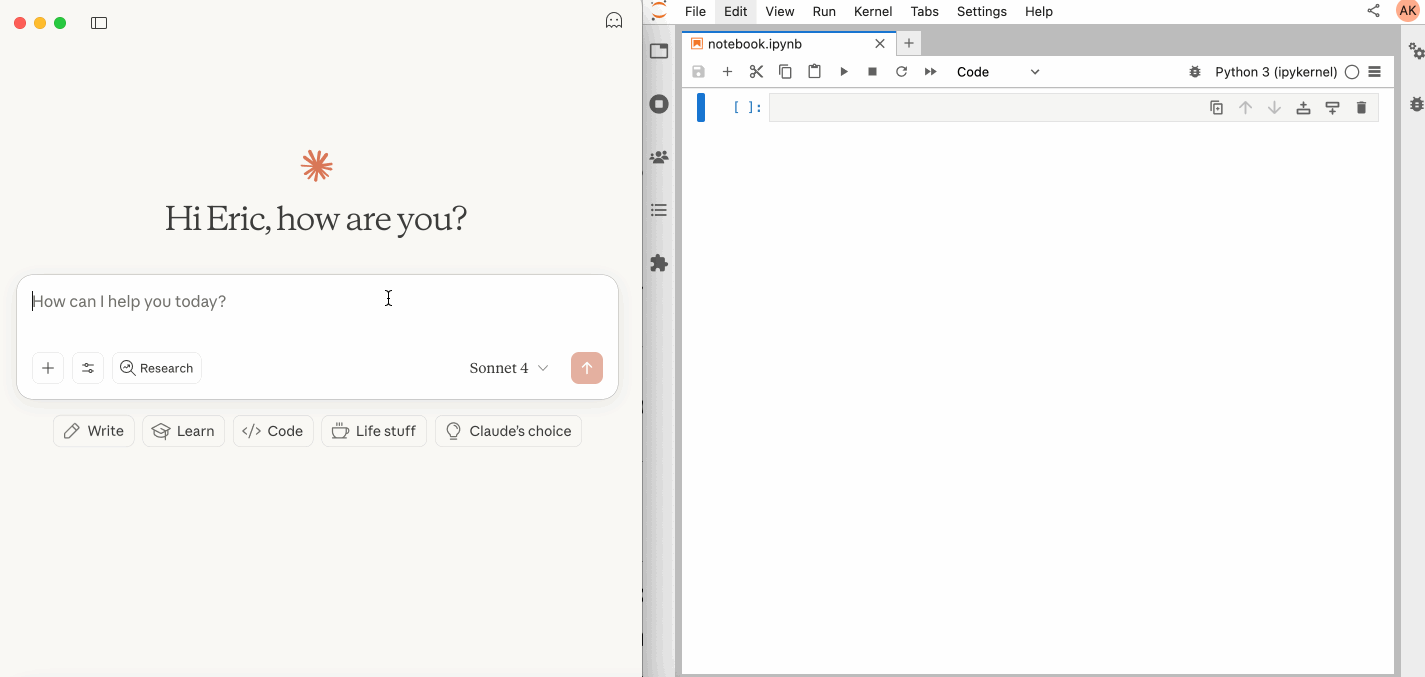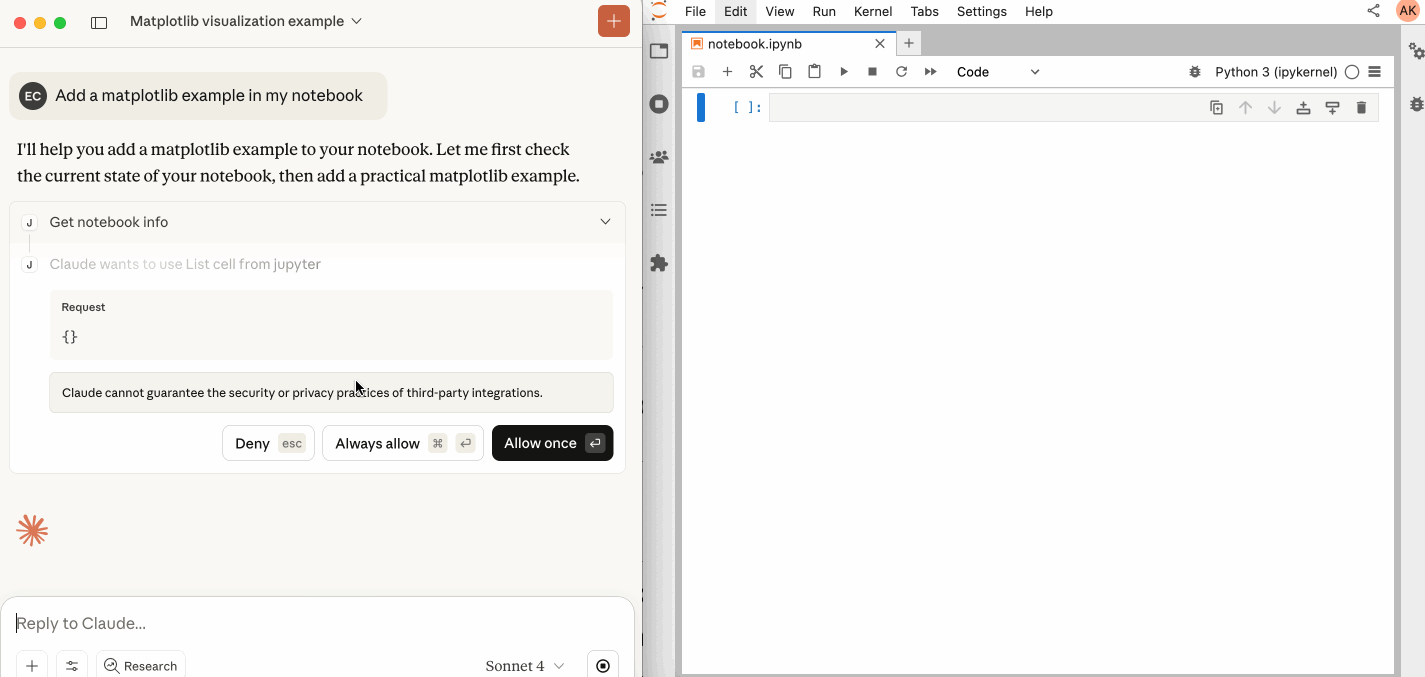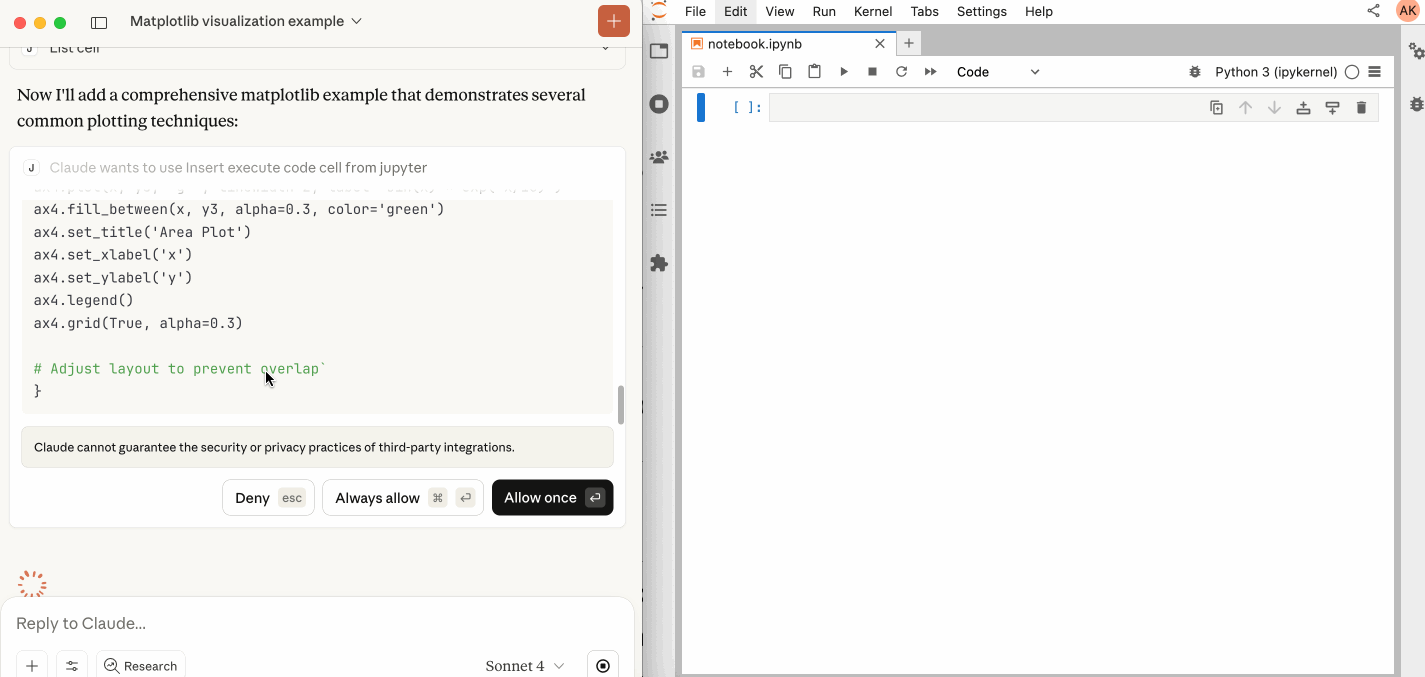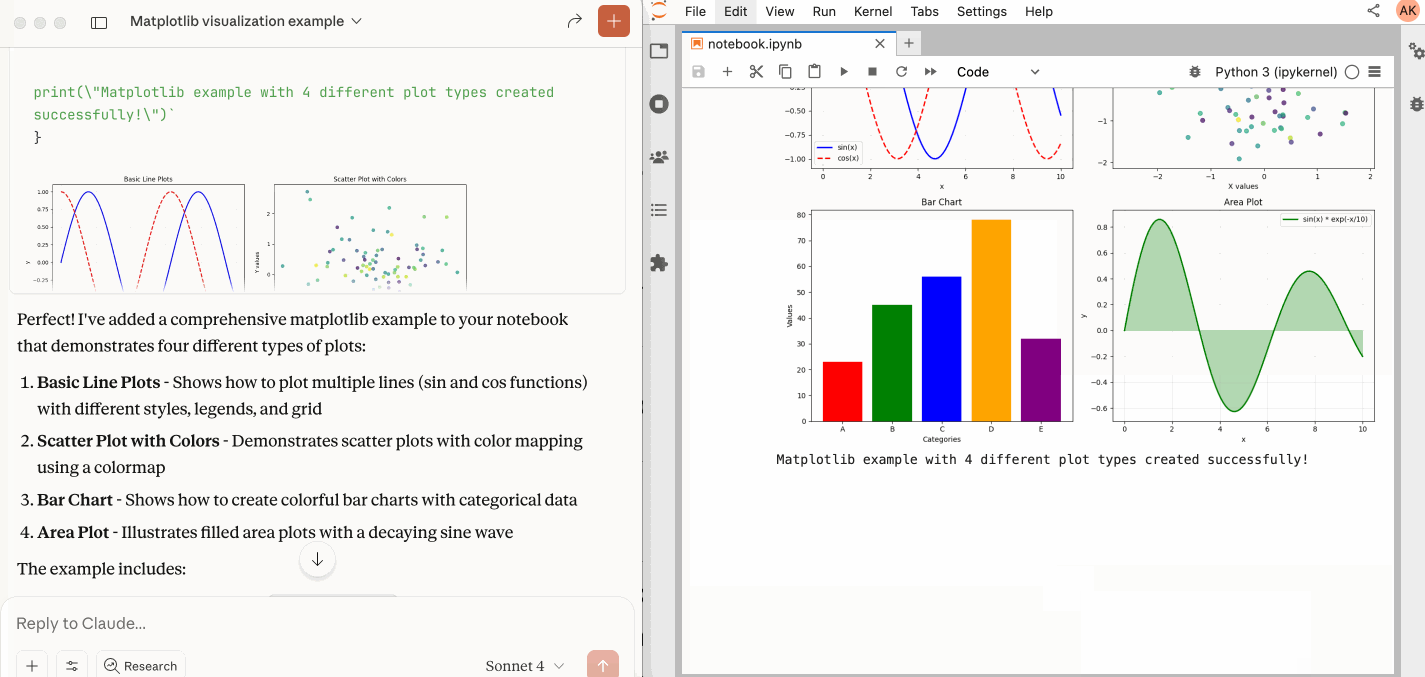
🛠️ This MCP offers multiple tools such as insert_cell, execute_cell, list_files, read_cell, and more, enabling advanced interactions with Jupyter notebooks. Explore our tools documentation to learn about all the tools powering Jupyter MCP Server.
🏁 Getting Started
For comprehensive setup instructions—including Streamable HTTP transport and advanced configuration—check out our documentation. Or, get started quickly with JupyterLab and stdio transport here below.
1. Set Up Your Environment
pip install jupyterlab==4.4.1 jupyter-collaboration==4.0.2 ipykernel
pip uninstall -y pycrdt datalayer_pycrdt
pip install datalayer_pycrdt==0.12.17
2. Start JupyterLab
# make jupyterlab
jupyter lab --port 8888 --IdentityProvider.token MY_TOKEN --ip 0.0.0.0
[!NOTE] If you are running notebooks through JupyterHub instead of JupyterLab as above, you should:
- Set the environment variable
JUPYTERHUB_ALLOW_TOKEN_IN_URL=1in the single-user environment.- Ensure your API token (
MY_TOKEN) is created withaccess:serversscope in the Hub.
3. Configure Your Preferred MCP Client
[!TIP]
Ensure the
portof theDOCUMENT_URLandRUNTIME_URLmatch those used in thejupyter labcommand.In a basic setup,
DOCUMENT_URLandRUNTIME_URLare the same.DOCUMENT_TOKEN, andRUNTIME_TOKENare also the same and is actually the Jupyter Token.The
DOCUMENT_IDparameter specifies the path to the notebook you want to connect to. It should be relative to the directory where JupyterLab was started.
- Optional: If you omit
DOCUMENT_ID, the MCP client can automatically list all available notebooks on the Jupyter server, allowing you to select one interactively via your prompts.- Flexible: Even if you set
DOCUMENT_ID, the MCP client can still browse, list, switch to, or even create new notebooks at any time.
You can choose between two deployment methods: uvx (lightweight and faster, recommended for first try) or Docker (recommended for production).
pip install uv
uv --version
# should be 0.6.14 or higher
see more details on uv installation
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["jupyter-mcp-server"],
"env": {
"DOCUMENT_URL": "http://localhost:8888",
"DOCUMENT_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"DOCUMENT_ID": "notebook.ipynb",
"RUNTIME_URL": "http://localhost:8888",
"RUNTIME_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}
MacOS and Windows
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run", "-i", "--rm",
"-e", "DOCUMENT_URL",
"-e", "DOCUMENT_TOKEN",
"-e", "DOCUMENT_ID",
"-e", "RUNTIME_URL",
"-e", "RUNTIME_TOKEN",
"-e", "ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT",
"datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server:latest"
],
"env": {
"DOCUMENT_URL": "http://host.docker.internal:8888",
"DOCUMENT_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"DOCUMENT_ID": "notebook.ipynb",
"RUNTIME_URL": "http://host.docker.internal:8888",
"RUNTIME_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}
Linux
{
"mcpServers": {
"jupyter": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run", "-i", "--rm",
"-e", "DOCUMENT_URL",
"-e", "DOCUMENT_TOKEN",
"-e", "DOCUMENT_ID",
"-e", "RUNTIME_URL",
"-e", "RUNTIME_TOKEN",
"-e", "ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT",
"--network=host",
"datalayer/jupyter-mcp-server:latest"
],
"env": {
"DOCUMENT_URL": "http://localhost:8888",
"DOCUMENT_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"DOCUMENT_ID": "notebook.ipynb",
"RUNTIME_URL": "http://localhost:8888",
"RUNTIME_TOKEN": "MY_TOKEN",
"ALLOW_IMG_OUTPUT": "true"
}
}
}
}
For detailed instructions on configuring various MCP clients—including Claude Desktop, VS Code, Cursor, Cline, and Windsurf — see the Clients documentation.
📚 Resources
Looking for blog posts, videos, or other materials about Jupyter MCP Server?
👉 Visit the Resources section.
Jupyter MCP Server Reviews
Login Required
Please log in to share your review and rating for this MCP.
Similar MCP Servers like Jupyter MCP Server
Explore related MCPs that share similar capabilities and solve comparable challenges
Git
Officialby modelcontextprotocol
A Model Context Protocol server for Git repository interaction and automation.
Zed
OfficialClientby zed-industries
A high‑performance, multiplayer code editor designed for speed and collaboration.
Everything
Officialby modelcontextprotocol
Model Context Protocol Servers
Time
Officialby modelcontextprotocol
A Model Context Protocol server that provides time and timezone conversion capabilities.
Cline
OfficialClientby cline
An autonomous coding assistant that can create and edit files, execute terminal commands, and interact with a browser directly from your IDE, operating step‑by‑step with explicit user permission.
Context7 MCP
Officialby upstash
Provides up-to-date, version‑specific library documentation and code examples directly inside LLM prompts, eliminating outdated information and hallucinated APIs.
Daytona
by daytonaio
Provides a secure, elastic infrastructure that creates isolated sandboxes for running AI‑generated code with sub‑90 ms startup, unlimited persistence, and OCI/Docker compatibility.
Continue
OfficialClientby continuedev
Enables faster shipping of code by integrating continuous AI agents across IDEs, terminals, and CI pipelines, offering chat, edit, autocomplete, and customizable agent workflows.
GitHub MCP Server
by github
Connects AI tools directly to GitHub, enabling natural‑language interactions for repository browsing, issue and pull‑request management, CI/CD monitoring, code‑security analysis, and team collaboration.


